
Analyzing Deformation Causes in Metal Injection Moulding (MIM) Post-Sintering: A Comprehensive Guide
1. Introduction to Metal Injection Moulding (MIM) Deformation Post-Sintering:
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a vital process in modern manufacturing, known for its precision and efficiency in producing complex parts. However, deformation post-sintering remains a significant challenge, impacting the dimensional accuracy and overall quality of the final product. This article delves into the causes of such deformations and presents effective strategies to mitigate them.
2. Understanding the Causes of Post-Sintering Deformation:
a. Material Factors:
- Consistency in Injection Feedstock: Variations in material batches can lead to defects during moulding and deformation during sintering.
- Effects of Powder Segregation and Binder Systems: Segregation of powder and binders can cause uneven density, leading to deformation during sintering.
- Impact of Sintering Temperature and Powder Load: Higher temperatures and powder loads can minimize deformation, while lower values can increase it.
b. Mold Design Considerations:
- Uniform Wall Thickness: Uneven wall thickness can lead to differential shrinkage and deformation.
- Reinforcing Ribs: While they strengthen parts, improper design can lead to warping and stress concentration.
- Gate and Cooling Channel Design: Inappropriate gate and cooling designs can lead to uneven shrinkage and deformation.
- Ejector Pin Design: Improper ejector pin design can cause deformation during part ejection.
3. Sintering Support and Process Stability in MIM:
In Metal Injection Molding, the sintering stage is critical for determining the final properties and dimensions of the part. Proper support and process control during this phase are paramount to minimize deformation. This section explores the nuances of sintering support and the importance of maintaining process stability to ensure the integrity of MIM parts.
a. Importance of Sintering Support:
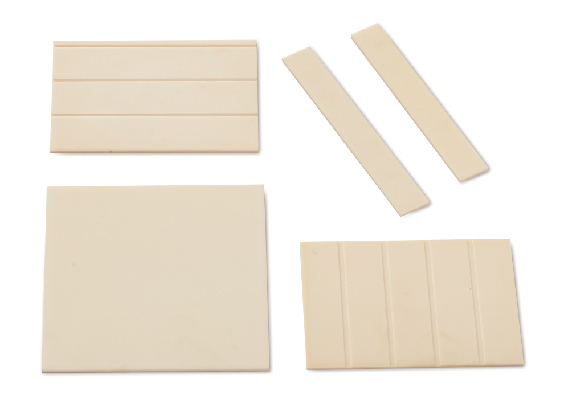
- Support Strategies: Implementing appropriate support structures or fixtures during sintering can significantly reduce the risk of warping or distortion, especially for complex geometries or thin-walled sections. For effective support solutions, refer to Moat City’s range of kiln furniture and furnace support trays, specifically designed to enhance the sintering process in MIM.
- Material Considerations for Support: The choice of support materials plays a crucial role. Materials with similar thermal expansion properties to the MIM part can reduce stress and deformation. Our kiln furniture and support trays are crafted to complement a wide range of MIM materials, ensuring optimal performance.
b. Process Stability:
- Uniform Heating: Ensuring uniform heating throughout the sintering furnace is crucial for consistent part quality and dimensional accuracy.
- Controlled Atmosphere: Maintaining a controlled atmosphere within the sintering furnace can prevent oxidation and other chemical reactions that might compromise the part’s integrity.
4. Mitigation Strategies and Best Practices for Reducing Deformation in MIM:
Addressing the challenge of deformation in MIM parts requires a multi-faceted approach. This section outlines key strategies and best practices aimed at minimizing deformation at each stage of the MIM process.
a. Material and Feedstock Optimization:
- Homogeneous Mix: Ensuring a homogenous mix of metal powder and binder in the feedstock is essential to prevent uneven shrinkage during sintering.
- Particle Size Distribution: Optimal particle size distribution in the metal powder can enhance packing density and reduce deformation risks.
b. Advanced Mold Design Techniques:
- Simulation-Driven Design: Utilizing advanced simulation tools to predict and mitigate potential deformation during the design phase can lead to more robust mold designs.
- Stress Analysis: Conducting stress analysis on mould designs helps identify areas prone to deformation, allowing for preemptive design modifications.
c. Sintering Process Control:
- Temperature Ramp Rates: Optimizing temperature ramp rates to balance sintering kinetics and part integrity can significantly reduce deformation.
- Real-time Monitoring: Implementing real-time monitoring systems in sintering furnaces can provide critical data for ensuring process consistency and identifying potential issues early.
5. Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the causes of deformation in MIM post-sintering is essential for manufacturing high-quality, precision components. A comprehensive approach involving material consistency, mould design optimization, and controlled sintering processes is key to minimizing deformation and enhancing product quality.
6. Contact Details:
For more information on Metal Injection Molding (MIM) and professional assistance, please contact us.
Email: rongqi.chen@moatcity.com
Web: www.moatcity.com
WhatsApp: +447983626714
We’re eager to assist with your MIM needs.





Leave a Reply