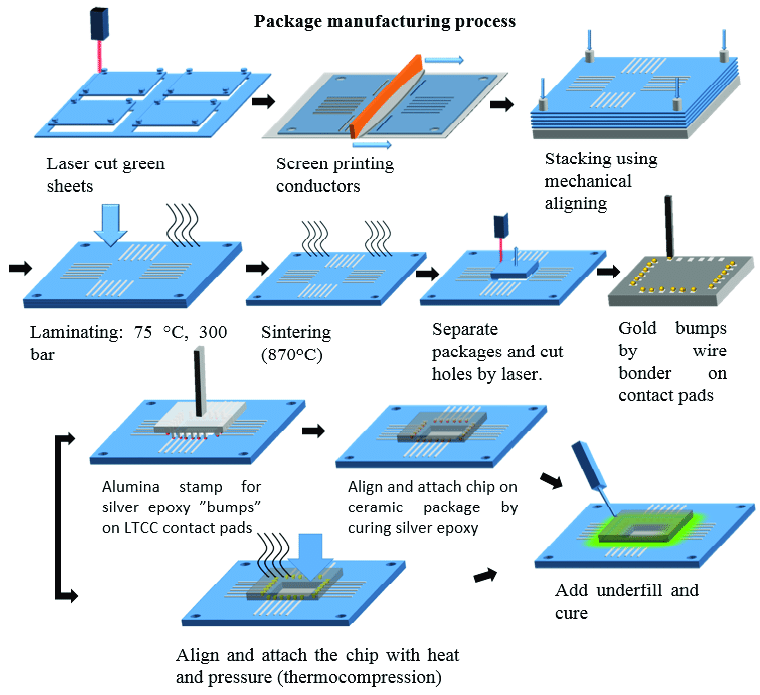
Navigating the Challenges in LTCC Sintering: A Professional Insight
Challenges in LTCC Sintering:
Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics (LTCC) technology has revolutionized the field of electronic packaging, offering unparalleled advantages in terms of device miniaturization, performance, and integration capabilities. Despite its significant contributions to the advancement of compact, high-performance electronic devices, the LTCC sintering process, a critical phase in LTCC fabrication, presents a unique set of challenges. This professional blog delves into these challenges, exploring their implications and discussing potential strategies for overcoming them.
Challenge 1: Thermal Stress Management
One of the primary challenges in LTCC sintering is managing thermal stress. The sintering process involves firing ceramic layers and embedded conductive materials at high temperatures to achieve densification and coalescence. However, the differential thermal expansion between various materials can induce stress, leading to warping, cracking, or delamination of the layers. This not only affects the structural integrity of the LTCC device but also its electrical performance.
Strategies for Overcoming: Careful design of the LTCC stack, including the selection of materials with compatible thermal expansion coefficients and the use of stress-relieving features, can mitigate thermal stress. Additionally, optimizing the sintering profile to control the heating and cooling rates can help minimize stress build-up.
Challenges in LTCC Sintering:
Challenge 2: Dimensional Control and Shrinkage
Achieving precise dimensional control is another significant challenge in LTCC sintering. All ceramic materials undergo shrinkage during sintering, which can be difficult to predict and control. Uniform shrinkage is crucial for the final device’s dimensional accuracy, as non-uniform shrinkage can lead to misalignment of layers and embedded components, affecting the device’s functionality.
Strategies for Overcoming: Implementing a thorough understanding of the shrinkage characteristics of the LTCC material and adjusting the design dimensions accordingly is essential. Employing sintering aids and controlling the sintering atmosphere can also help achieve more uniform and predictable shrinkage.
Challenges in LTCC Sintering:
Challenge 3: Sintering Atmosphere Control
The atmosphere within the kiln during sintering plays a critical role in determining the LTCC’s final properties. Oxidizing or reducing atmospheres can significantly affect the behavior of the conductive materials embedded within the LTCC, potentially altering their electrical properties.
Strategies for Overcoming: Precise control of the kiln atmosphere, through the use of gas flow controls and monitoring systems, is essential. Selecting the appropriate sintering atmosphere for the specific materials involved can prevent undesired chemical reactions and ensure the integrity of the conductive paths.
Challenge 4: Integration of Multiple Materials
LTCC technology enables the integration of a wide range of materials (ceramics, metals, etc.) to create devices with complex functionalities. However, the disparate properties of these materials, such as their sintering temperatures and chemical compatibilities, pose a significant challenge. Ensuring that all materials co-sinter effectively without adversely affecting each other is crucial for the device’s performance.
Strategies for Overcoming: Material selection is key. Using materials specifically formulated for LTCC applications, which have been engineered to sinter at compatible temperatures and under similar conditions, can alleviate many integration challenges. Additionally, the use of buffer layers or barrier coatings can prevent adverse interactions between materials.
Challenge 5: Scale-up and Reproducibility
Scaling up the LTCC sintering process from prototype to mass production while maintaining consistency and reproducibility is a formidable challenge. Process parameters that work for small-scale production may not directly translate to larger scales due to differences in thermal gradients, kiln loading, and atmosphere uniformity.
Strategies for Overcoming: Rigorous process optimization and control are crucial for scaling up LTCC sintering. This includes the use of scalable kiln designs, precise control systems for temperature and atmosphere, and robust quality control measures to ensure consistency across production batches.
Conclusion
While the challenges in LTCC sintering are significant, they are not insurmountable. Through careful material selection, process optimization, and innovative engineering solutions, manufacturers can overcome these hurdles, unlocking the full potential of LTCC technology. As the demand for smaller, more integrated electronic devices continues to grow, the importance of mastering LTCC sintering processes will only increase, driving further innovation in this exciting field.


![Silicon Carbide Board [MH-KX-SiC]](https://moatcity.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/1728636817408.png)

Leave a Reply